The use of innovative optical devices to optimise treatment of burns patients
Timely and accurate estimation of the surface area and depth of a burn injury is essential for determining appropriate management. Inappropriate or inadequate treatment may result in complications and increased societal costs. Burn depth is determined by making a subjective assessment of the characteristics of the injury. Some objective methods are available (e.g., biopsy and histology, thermography and laser Doppler), but these are cumbersome. In assessing burn wounds, laser Doppler imaging (LDI) ., is currently the most widely used validated noninvasive measurement tool for ..
In this project a newer laser-based technique, laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI), was tested in specialised burn care. The LSCI works with the similar principle and might become an alternative for LDI. LSCI has some advantages over LDI such as higher spatial resolution, much easier to position, no valuable time wasted on setting up the instrument, easy to take several images of burns that have a large surface area and/or much curvature, faster measurements, fraction of the time needed for getting a high-quality measurement, able to follow changes in the perfusion/microcirculation in real time. In contrast to the LDI, the LSCI has not been validated in terms of a diagnostic tool for stratifying the severity of a burn.
Therefore, the aim of this project was to validate the LSCI. Results of the LSCI an LDI are compared in 15 volunteers and 50 patients with burn injuries. Cut off values for the diagnosis of burn wound depth were calculated and are ready to be included in the software of the LSCI. The next step will be some adaptations of the system and implement the LSCI in clinical practice of burn patients to optimise the diagnostic process. In addition, Incident Dark field Imaging (IDF), with a hand held microscopy was used to evaluate changes in the microcirculation under the tongue in 22 patients with severe burn injuries. With this technique, resuscitation in patients with severe burn injuries in the first 24 hours after injury can be monitored and improved.
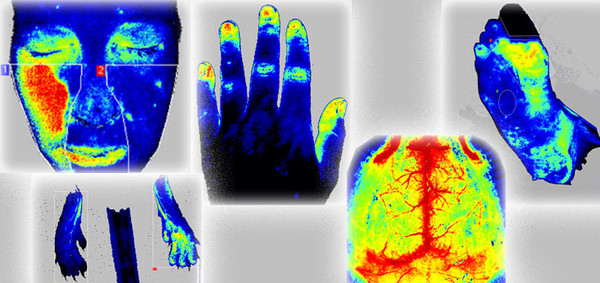 Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging.
Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging.
Source: Perimed.



