The development of predictive epigenetic biomarkers to guide successful treatment of CD
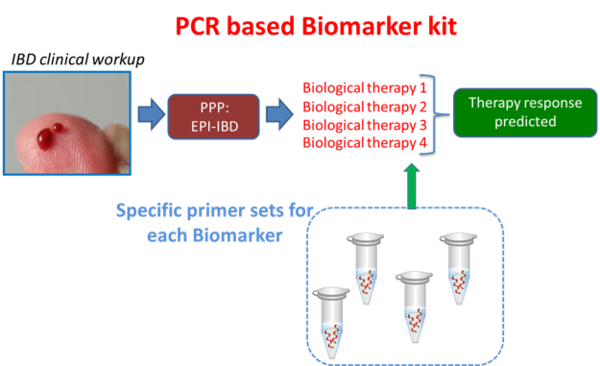
In this project, GenDX and AMC are working together to develop a method based on blood samples, biomarkers on the DNA to predict optimal treatment of patients with Crohn's disease (CD).
CD is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease for which no cure is possible. CD affects more than 1 million people in Europe and North America. The use of biological drugs such as anti-TNF antibodies has improved care for patients with CD, as these biological drugs are the only medical interventions that change the natural course of the disease. In CD, all approved biological antibodies are antibodies that neutralize an important immunological process regulator (TNF, IL-23, integrin a4b7). All in all, intensive research, up to 70% adalimumab (ADA), the anti-integrin vedoluzimab (VEDO) and the anti-p40 antibody ustekinumab (USTE)). At the moment it is impossible to predict which patients respond to one of the biological treatments, which means that a trial and error approach is often used. The result is that it can take a very long time before effective treatment is found and often leads to complications such as fists, abscess and stenosis, which are indicated by surgery.
In this project it is aimed to make the treatment of CD possible by identifying the DNA biomarkers that predict the response to treatment. The assumption is that this complex disease is different for every patient and therefore the response to therapy also depends on various factors. In this proposal the latest technology is applied to analyze the blood and tissue cell composition and gene expression on a single cell level. It is important that biomarkers will be detected that are already present before the therapy is started, so that they can be used to predict the therapy response, supporting the clinician's choice for a specific biological treatment.
Patients will be strictly selected and the response to treatment will be documented with the help of endoscopy and symptom scores. The results of this project will lead to more insight into the development of CD, but also to the development of a biomarker tool, which can be used to optimize individual CD patient treatment in hospitals worldwide.
This collaboration project is co-funded by the PPP Allowance made available by Health~Holland, Top Sector Life Sciences & Health, to AMC to stimulate public-private partnerships. For questions, please contact AMC directly via the following email address tki@ixa.nl.


