Italy has the third-largest national economy in the European Union. It is the tenth-largest exporter in the world, with its closest trade ties being with other countries within the European Union, with whom it conducts about 59% of its total trade. However, Italy was among the countries hit hardest by the Great Recession of 2008-2009 and the subsequent European debt crisis, from which it is still recovering. Recently, the European Commission has endorsed Italy’s National Recovery and Resiliency Plan, which will disburse €68.9 billion in grants and €122.6 billion in loans. This financing will support the implementation of the crucial investment and reform measures that are outlined within this plan, enabling Italy to emerge stronger from the COVID-19 pandemic.
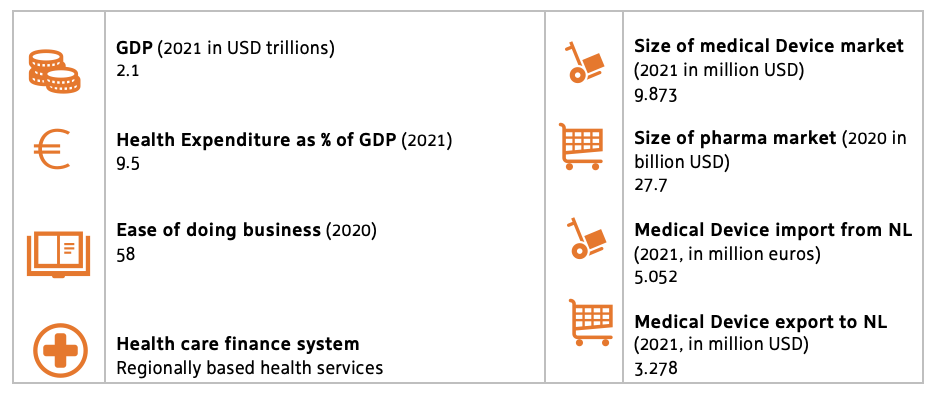
Italy has a higher life expectancy at birth than most of the OECD and EU countries, achieving this while keeping its healthcare spending to GDP at lower levels than the EU average. Although life expectancy might be determined by other factors (quality of food, water, lifestyle, etc.), the provision of healthcare has undoubtedly played a role. Nevertheless, Italy presents some critical structural problems which have become evident in the wake of the pandemic. Hospitals have proven to be unable to react to significant shocks. This is due to several factors: a low number of nurses and specific medical specialists, outdated technologies and lacking implementation of telemedicine and home-care. These, combined with an ageing population, create a situation that put the Italian National and Regional Health Services under unsustainable pressure throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
The National Recovery and Resilience Plan (PNRR), set forth by Italy and endorsed by the European Commission, outlines the reforms and investments to be implemented by 2026 that will enable Italy to emerge stronger from the COVID-19 pandemic. Within this plan, €15.6 billion (8.16% of total PNRR amount) has been allocated towards the mission of improving the National Health System by modernising facilities, guaranteeing fair access to treatment and promoting R&D.
From the perspective of the Netherlands the following market trends are of interest:
Trade
- Healthy Living & Ageing.
- Italy’s population is rapidly ageing, increasingly straining its (long-term) care infrastructure. Under the PNRR, funds will de devoted to this issue (e.g. €4 billion is devoted to Home-Integrated Assistance in coordination wth the NHS). Furthermore, by 2026, 1,288 Community Homes (Case della Comunità) will be built. A €2 billion investment is planned for these homes.
- The Digital Transformation of Health and Care
- COVID-19 has underlined the need for effective digital health strategies and efficient implementation of these strategies. Under the PNRR, funds will be devoted to technological and digital updating. Specifically, the focus will be on renewing digital systems, ensuring dissemination and uptake of universal Electronic Health Records, and providing Essential Levels of Assistance throughout Italy.
- Infrastructure.
- Under the PNRR package, €7 billion is to be alocated towards the development of hospitals, in addition to community health services and telemedicine. Priorities include strengthening intensive and sub-intensive care units, modernising emergency rooms, and facilitating the purchase of new ambulances for transport.
- Public health.
- Biopharma.
- Italy is the third ranked pharmaceutical market in Europe (2019), behind Germany and France, with a total revenue of €29.7 billion. Large investments have been made in innovation of the entire supply chain.
Research and Innovation
1. Under the PNRR, one of the focus areas is Hospital and Healthcare Infrastructure. The improvement of hospital infrastructure and respective technology needed to promote research and innovation falls under this pillar. Concrete milestones include:
- Building 381 community hospitals for patients requiring short-term stays.
- Creation of 5 operational centers, 4 innovative technology R&D centers and 1 strategic infrastructure center dedicated to the response to future pandemics.
- Launch of 1,288 Community Health Houses to strengthen home-care and effectively integrate health and social services.
- Home-care provided to 10% of the over-65 population with chronic diseases or those who are not self-sufficient.
- Using telemedicine, i.e. home automation and digitalisation to build a shared home-care model.
- Launch 602 Local Operational Centers and a new training system at each Local Health Authority to manage home services.
2. Another of the focus areas under the PNRR is Technology & Digital Updating. The renewal of digital systems, ensuring dissemination of the Electronic Health Record (ESF) and providing Essential Levels of Assistance throughout Italy falls under this pillar. Concrete milestones include:
- Digitalisation of 280 health facilities.
- Acquisition of the latest technologies for CT scans MRIs and other medical examinations.
- Structural upgrades for hospitals with renewed intensive and semi-intensive care beds.
Invest
In Italy the Netherlands Foreign Investment Agency (NFIA/ Invest in Holland network) does not have a location. Our office in Paris is also supporting Southern Europe.
NFIA /Invest in Holland network is keen to welcome and assist foreign companies that contribute to the goal of the Netherlands in finding solutions that deliver better, affordable and sustainable healthcare and strengthen our Life Sciences & health ecosystems.
Regional priorities
During the validation session with Dutch SMEs active in the Life Science & Health sector doing business or wanting to do business in Italy, the Northern and Central region were of most interest. The Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions are the most important for the (bio)medical industry, with the Milano Innovation District (MIND) Lombardy is getting more and more the centre of Italian life sciences willing to apply knowledge and data in new products.
Overview milestones & flagships.
- G2G (MoU, state visits)
- Trade (PIBs, market study E-health (2019)
- Innovate (joint R&D projects, specific bilateral calls)
- Invest (significant investments in the Dutch LSH sector
The way forward
During the validation session with Dutch SMEs active in the Life Sciences & Health sector doing business or wanting to do business in Italy, matchmaking came out as the type of support most relevant. Besides, trade missions, trade fairs, market reports funding opportunities and country updates were mentioned as relevant types of support. Participants had most interest in meeting agents and distributors, elderly care facilities, hospitals, regulatory authorities and branch associations. The structural barriers that participants experienced were mostly related to finding a good distributor, as well as knowledge on market entry, laws and regulation and difficulties to reach key decision makers.
Proposed activities 2021/2022
- Health~Holland Visitors Conference and World of Health Care
- Exposanità (4-7 May 2022)
