Canada is the 10th largest economy in the world and an important trading partner for the European Union and the Netherlands. The Comprehensive and Economic Trade Agreement, or CETA, is a trade deal between the EU and Canada. It cuts tariffs and makes it easier to export goods and services, benefitting people and businesses in both the EU and Canada. Canada and the Netherlands are important investment and innovation partners. Canada has a universal healthcare system with public health insurance that is managed at a decentralised level by the individual provinces and territories.
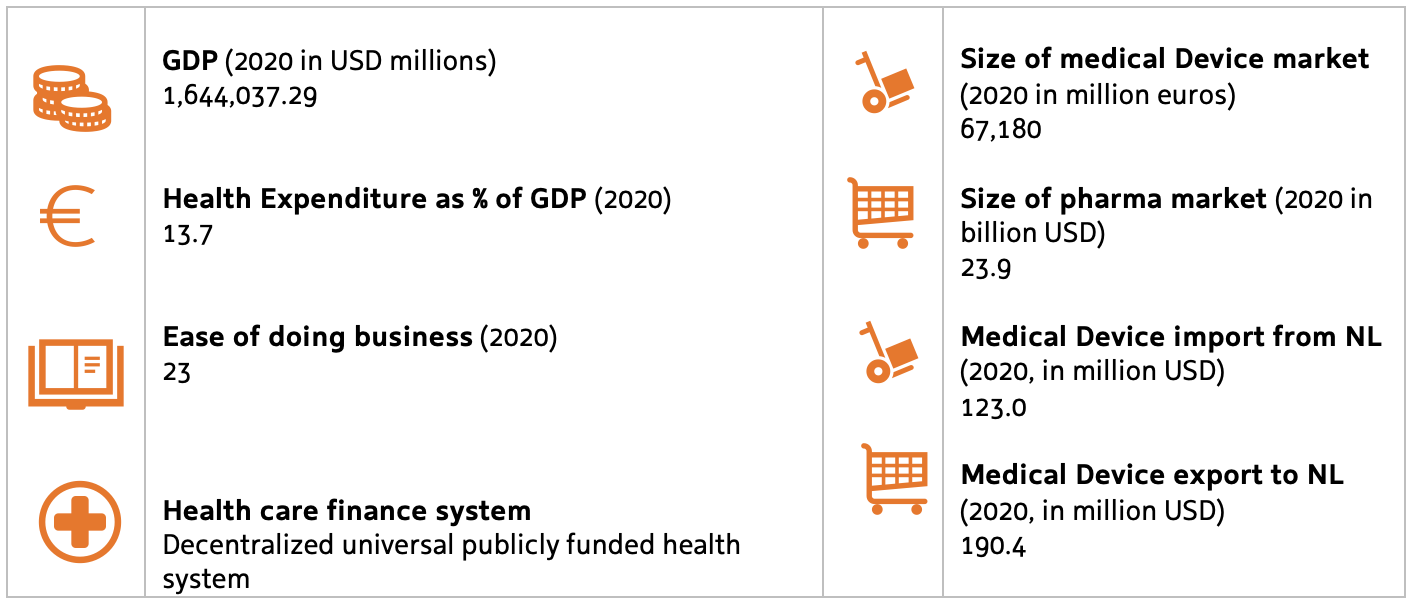
Canada has a highly developed healthcare system and faces issues that are common for developed economies: an aging population, increased healthcare expenditures, shortage of healthcare workers, and long waiting times. Canada’s life sciences sector boasts a solid track record of healthcare innovation characterized by cutting-edge research, innovative thinking and cross-industry collaboration.
From the perspective of the Netherlands the following market trends are of interest:
Trade
· Mobility & vitality. Canada’s population is rapidly ageing, increasingly straining its (long-term) care infrastructure. Canada is investing to modernise existing infrastructure and develop extra capacity in elderly care facilities. However, the costs to build, maintain and operate sufficient infrastructure for the elderly population exceeds desired budgets. Therefore, there is also interest in expanding homecare services.
· Digital health. One of the major interventions the Canadian health system aspires to achieve to make itself more efficient and durable is the widescale adoption of digital health solutions by healthcare providers and recipients.
· Biopharma. The Canadian pharmaceutical market is a top 10 global player in both the development and production of innovative technologies. R&D partnerships with the Canadian private sector and research institutes therefore offer opportunities for the Netherlands.
· Medical devices. In a context where Canada (like other Western countries) needs to stagnate / decrease costs in order to keep its developed health system sustainable, there exists a demand for Smart Solutions which can increase the efficiency of health services.
· Public health. Canada’s public health system is being challenged on many fronts. There is an increasing need for ongoing training to allow practitioners to adapt their skills and strategies to incorporate the advocacy and community mobilisation associated with population health approaches. There is also a need to implement measures that evaluate the effectiveness of public health interventions. However, Canada’s system is focused primarily on acute care, rather than investing in long-term, preventative measures. Increased focus is being placed upon physical and mental health, as well as public health emergency preparedness and response.
Research & innovation
· In 2020, the Canadian government announced an investment of $240.5 million to increase access to virtual services and digital tools to support Canadians' health and wellbeing .
· There is wide recognition that Canada has lagged behind many peer nations in the development of health infrastructure and in its uptake of digital healthcare innovations such as virtual care, home monitoring, and remote-control robotic interventions .
· In 2017, the Government of Canada appointed CIFAR to develop and lead a $125 million Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy, the world’s first national AI strategy. The Strategy enabled the establishment of new, independent research institutes in Edmonton (Amii), Montreal (Mila), and Toronto (the Vector Institute) in partnership with provinces and the private sector3.
COVID-19 caused an uptake in the nascent Canadian market for telehealth applications. Platforms such as the Ontario Telemedicine Network doubled in size, from 1.4 million patients (2019-2020 fiscal year) to 2.8 million patients (2020-2021 fiscal year). Between March and July 2020, office visits in Ontario declined by nearly 80 percent and virtual care increased 56-fold, comprising 71 percent of primary care physician visits, according to a study by the Canadian Medical Association Journal . It remains to be seen whether this growth can be sustained now that the pandemic is winding down.
Canada is part of the EUREKA, the world’s biggest public network for international cooperation in R&D and innovation. Which makes it possible for Dutch and Canadian SMEs, companies and research organisations to set up bilateral and multilateral industry/market driven R&D collaborations and apply for funding, e.g. Eurostars or Clusters (national contact points: National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO).
Invest
· The Canadian life sciences sector saw success in public equity markets, with financing topping $4 billion, including initial public offerings by AbCellera Biologics (monoclonal antibodies), MindBeacon (e-health), Fusion Pharmaceuticals (radiopharmaceuticals), Repare Therapeutics (oncology), Think Research (healthcare software), and Aurinia Pharmaceuticals (autoimmune diseases).
· Over the first nine months of 2020, Canadian biotech and life sciences companies raised more than 1 billion CAD in venture capital, surpassing the 2019 record of 1.085 billion CAD, according to the Canadian Venture Capital and Private Equity Association.
· Canada boasts strong clusters of start-ups and scale-ups in Ontario/GTA, Vancouver Metropolitan Area and East Québec. Many of Canada’s life sciences companies are small compared to their USA counterparts. In 2018, Canada had nearly 8,000 companies with more than 190,000 employees, for an average of 24 employees per company, according to a report by the non-profit BioTalent Canada.
The Life sciences and health metropolis of Netherlands offers a geostrategic location for Canadian companies looking to build their business across Europe. Furthermore the Netherlands offers a thriving business climate, political and economic stability with a population highly proficient in the English Language. Many companies were previously interested in the UK as a location, due to Brexit and the relocation of the EMA the Netherlands offers a strong alternative location with access to EU markets.
In Canada the Netherlands Foreign Investment Agency (NFIA) is located in Toronto. This office provide the first point of contact to support and promote investment opportunities for Canadian companies looking to connect with the Netherlands LSH eco-system. Together with the Invest in Holland Life Sciences & Health team the office is keen to welcome and assist foreign companies that contribute to the goal of the Netherlands in finding solutions that deliver better, affordable and sustainable healthcare and strengthen our Life Sciences & health ecosystems.
The Invest in Holland LSH team is a collaborative team of the NFIA, regional development agencies, several large cities and Holland International Distribution Council.
Regional priorities
The main regions of interest are Ontario (Ottawa & Toronto), Quebec, and British Columbia (Vancouver). Below, an overview is given of key life science subsectors of interest per region, per province.
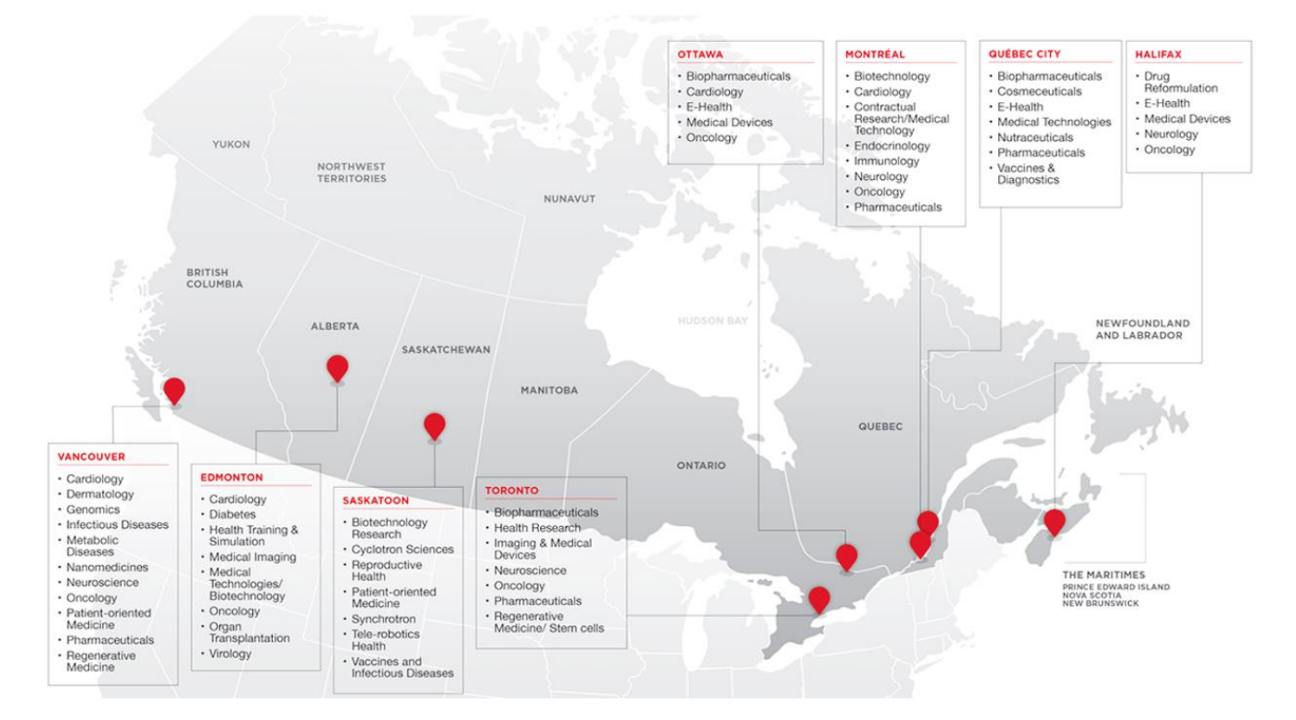
The interest of Dutch SMEs in Canada is focused primarily on digital health and mobility & vitality, with a specific focus on elderly care. Other potential value chains include: public health, biopharma and medical devices.
Most prominent NL value chains
1. The digital transformation of health and care: the application of both digital information and communication solutions to support and / or improve health and healthcare processes.
- Demonstrated (or expected) impact and activities
- One of the five key areas of focus for Canadian Life Sciences is harnessing digital health by creating a national digital health strategy featuring an interoperable digital health platform.
- Potential opportunities
- Virtual Care: the use of electronic means to reduce or replace face-to-face interaction, patient-centered care.
- Big Health Data: the ability to analyse large volumes of different types of data from a variety of sources that are continuously generated, for example using Artificial Intelligence.
- Technological Developments: includes robotics, 3d printing, virtual and augmented reality, nanotechnology, the Internet of Things (connected devices), health apps that run applications on smartphones and block chain technology.
Barriers:
- Difficulty to reach key stakeholders
- Local competition
- Each province (jurisdiction) has its own laws and regulation
Preferred region(s):
- Ontario
- Quebec
2. Healthy Living & Ageing
Demonstrated (or expected) impact and activities
By 2031, nearly twice as many older adults will require care. Long-term care is expected to reach 606,000 patients in 2031, up from 280,000 in 2019.
- Potential opportunities:
- Home care: virtually all Ontario seniors (91%) hope to stay in their own home or apartment as long as possible. This can be facilitated using solutions such as domotica, telemedicine, remote monitoring, personal emergency response, etc. as well as investment in publicly-funded home care.
- Improving quality of life: solutions focused on improving quality of life by implementing smart solutions, such as staying connected with family members and friends, digital physical therapy platforms, etc.
Barriers:
- Local & international competition
- Difficulty to reach key stakeholders
- Finding a good pilot project or distributor
- Each province (jurisdiction) has its own rules and regulations
Preferred region(s):
- British Columbia (Vancouver)
- Ontario
- Quebec
Overview milestones & flagships
- G2G (MoU, state visit)
- Trade (PIBs, Market studies)
- Innovate (joint R&D projects, specific bilateral calls)
- Invest (significant investments in the Dutch LSH sector)
Collective Activities to Canada
2015
- Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between MaRS Discovery District (Toronto, ON) and StartupDelta, aiming to help identify technologies created by ventures in each innovation hub.
- MoU between University of Toronto (Toronto, ON) and Utrecht University to promote cooperation in research and education
2016
- MoU between University of Western Ontario (London, ON) and Radboud University to foster the exchange of students and researchers, specifically focused on the theme brain, cognition and behaviour
2017
- MoU between McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and VU University Amsterdam to enhance research and education collaborations in health sciences, among other fields
2018
- MoU between Canada National Research Council (NRC) and NWO to enhance collaboration between innovation and R&D experts in areas of national priority, including healthcare and bio and life sciences.
- Visit OostNL to Health Innovation Week Toronto
- AmsterdaminBusiness and Health~Holland Health Mission to Toronto and Boston
- Visit OostNL on Digital Health and Smart Devices to Toronto (and Calgary)
2019
- MoU between McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and Maastricht University toward establishment of a doctoral program with a cotutelle agreement
- Study visit by MoH led by MoH Attaché in Washington, D.C. on Canada’s cannabis legalisation and regulation policies
- Trade mission Go4Export | OostNL on rehab technologies and smart ageing to Toronto and Waterloo
2020
- (Virtual) Medtech Mission & Matchmaking, WTC Twente and WTC Toronto
2021
- Life Sciences & Health Sector Study Ontario
- Creation of the Netherland-Canada Type 2 Diabetes Research Consortium between Maastricht Univeristy and Université de Sherbrooke (Sherbrooke, GQ), facilitated by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, Dutch Diabetes Research Foundation, ZonMw, and Health~Holland
2022
- Publication of Life Sciences & Health Market Study | Canada
- Launch of Life Sciences & Health Market Study | Canada in combination with the Health~Holland Digital Reconnect Canada
The way forward
During the validation session with Dutch SMEs active in the Life Sciences & Health sector doing business or wanting to do business in Canada, the following types of support were mentioned as most relevant to them:
- Matchmaking
- Trade mission
- Trade fair
- Market information / reports
Proposed activities 2023
- Trade mission September 2023
- Health~Holland Digital Reconnect Canada

